(→FTM Object Definitions) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The ''ftm.object'' external can be used to statically | + | The ''ftm.object'' external can be used to statically defin and name FTM objects, variables and constants. |
The graphical external has two text fields. | The graphical external has two text fields. | ||
The object or value definition is entered into the left text field. | The object or value definition is entered into the left text field. | ||
| − | + | In right field, a name can be given to the defined FTM object, constant or variable. | |
| + | The name can be used in [[expressions | FTM expressions]] using the '$'-syntax. | ||
Additional properties such as the scope of the object's name are defined in the inspector of the external. | Additional properties such as the scope of the object's name are defined in the inspector of the external. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
The following example defines a floating-point matrix (''fmat'' class) named ''myfmat'' and initializes it with random values: | The following example defines a floating-point matrix (''fmat'' class) named ''myfmat'' and initializes it with random values: | ||
| − | [[Image:Ftm.object-obj.jpg|frame|none| | + | [[Image:Ftm.object-obj.jpg|frame|none|definition of a floating-point matrix (''fmat'' class) named ''myfmat'' initialized with random values]] |
| − | definition of a floating-point matrix (''fmat'' class) named ''myfmat'' | ||
== Constant Definitions == | == Constant Definitions == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
For numeric constants the ''const'' keyword can be left out. | For numeric constants the ''const'' keyword can be left out. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Ftm.object-const.jpg|frame|none|definition of pi as an FTM constant and a symbol constant named ''label'']] | ||
== Variable Definitions == | == Variable Definitions == | ||
| + | To define FTM variables the keyword ''var'' is used as first argument in the ''ftm.object'' external: | ||
| + | * <'var'> [ <any: initial variable value> ] | ||
| + | |||
| + | When no initial value is given, the variable is initialized to 0. | ||
| + | |||
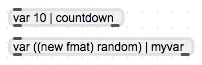
| + | [[Image:Ftm.object-var.jpg|frame|none|definition of variables initialized to different values]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:FAQ]] [[Category:FTM Documentation]] [[Category:fmat Class]] [[Category:ftm.object]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:25, 2 July 2010
The ftm.object external can be used to statically defin and name FTM objects, variables and constants. The graphical external has two text fields. The object or value definition is entered into the left text field. In right field, a name can be given to the defined FTM object, constant or variable. The name can be used in FTM expressions using the '$'-syntax.
Additional properties such as the scope of the object's name are defined in the inspector of the external.
FTM Object Definitions
For statically defining an FTM object with the ftm.object external the following syntax is required:
- <sym: class name> <list: instantiation arguments> [ , <list: initialization message> ... ]
The following example defines a floating-point matrix (fmat class) named myfmat and initializes it with random values:
Constant Definitions
Constants can be defined with the ftm.object external using the const keyword:
- [ <'const'> ] <any: constant value>
For numeric constants the const keyword can be left out.
Variable Definitions
To define FTM variables the keyword var is used as first argument in the ftm.object external:
- <'var'> [ <any: initial variable value> ]
When no initial value is given, the variable is initialized to 0.